CONFIDENCE AND COMPASSION
For Patients
SUPERIOR CARE AND SAFETY
For Patients
At CIRA, top-quality patient care is our primary focus. We are only a phone call away from your doctor when needed. CIRA radiologists provide rapid results on all radiological testing, ensuring that your doctor has the information he or she needs to provide you with the very best medical care. We call this the CIRA Radiologic Difference: delivering compassionate, high-quality care using the most advanced technology available, and the highest level of diagnostic interpretation – all for you.
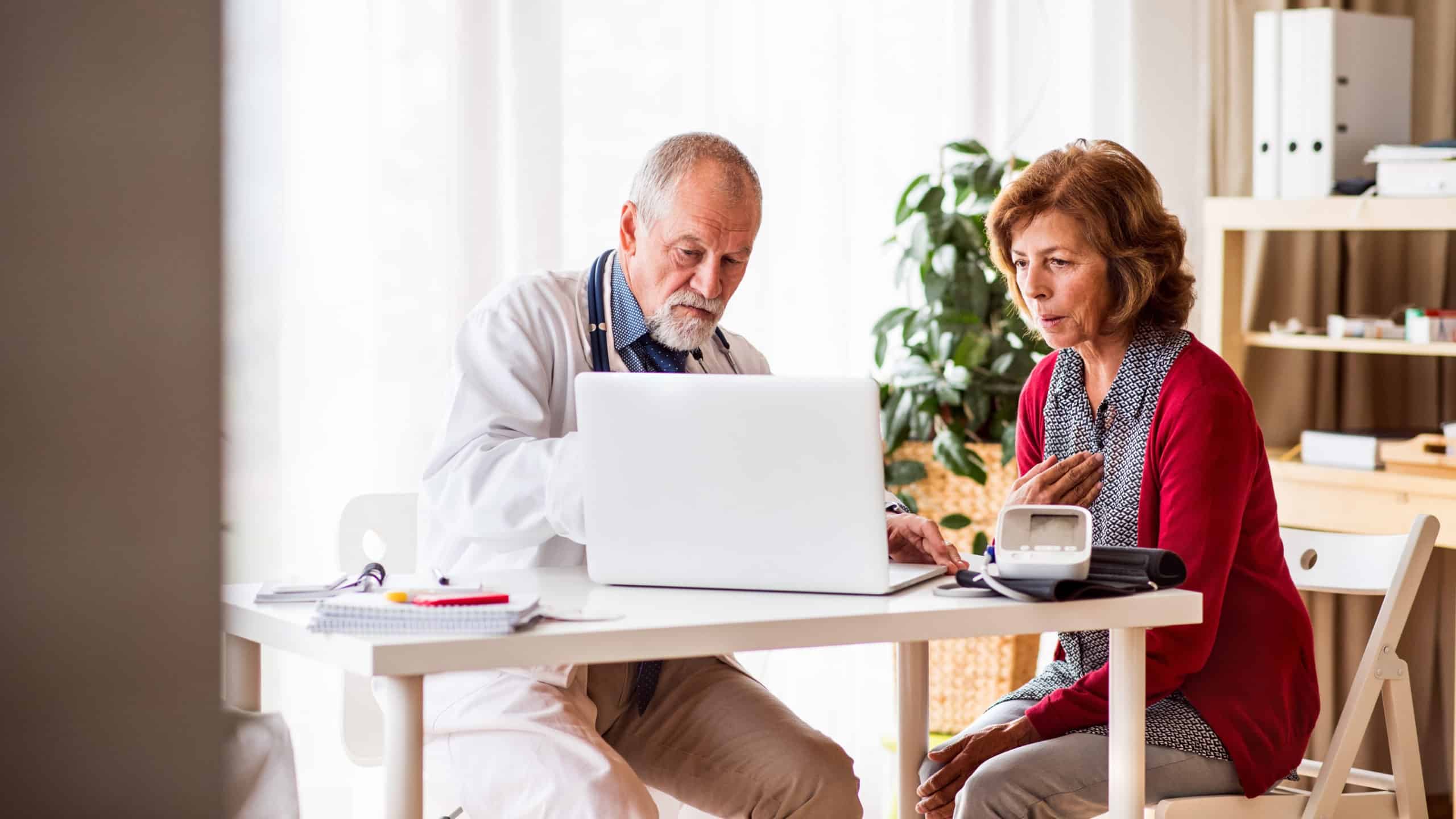

What to Expect
CT Scan
dexa
Mammography
pet
Ultrasound
x-ray
Radiology Resources and FAQ
RadiologyInfo.org tells you how various x-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, radiation therapy and other procedures are performed. It also addresses what you may experience and how
What Is a Radiologist?
Radiologists are medical doctors that specialize in diagnosing and treating injuries and diseases using medical imaging (radiology) procedures (exams/tests) such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT),
Radiation Doses in XRay and CT Exams Explained
Doctors use “effective dose” when they talk about the risk of radiation to the entire body. RadiologyInfo.org offers a helpful, thorough overview of X-Ray and
Types of Care and Providers
DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
Breast
(mammography)
Cardiothoracic
(Heart, lungs, and circulatory system)
Gastrointestinal/Genitourinary
(abdomen, reproductive, and urinary systems)
Musculoskeletal
(muscles and skeleton)
Neurological
(brain, nervous system, spine, head, and neck)
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
(imaging at the cellular and molecular level)
Pediatric
(imaging of children)
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY
Vascular and Interventional Radiology
Neurointerventional Surgery
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.